Games that develop fine motor skills in many ways. Development of motor skills in children
For the development of fine motor skills in children 4-5 years old, you need to perform simple exercises and massage the hands. Experts advise letting kids open and close jars, pour cereal from glass to glass, and teach them how to tie knots. All these games for the development of fine motor skills in children will not take much time, but the benefits will be undeniable, because the way a child knows how to coordinate his movements largely affects the development of his speech and thought centers.
The most important role in the development of the child is played by the development of fine motor skills and coordination of finger movements. Therefore, it is very important to engage with a child from an early age through special exercises, games and tasks for the development of fine motor skills. The development of fine motor skills at 4-5 years old affects the maturation of the speech and motor areas of the cerebral cortex, which are in close proximity to each other. By developing motor skills, we influence the intellectual development of the baby.
At this age, parents should carefully observe the child, because the harmless turning of the sheet when drawing or coloring indicates a rigid fixation of the brush. This can be checked as follows: ask the child to draw a circle with a diameter of about 5 cm. If he without much effort drew a circle of the desired diameter with one line, then you can be calm: he is fine with fine motor skills. If the child did not draw a circle, but a small oval and in several stages, while moving his hand, then this is already a violation of the coordinated movements of the hand.
Massage of the hands for the development of fine motor skills in children
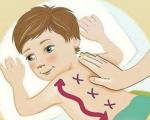
Massage of the hands has a beneficial effect on the development of fine motor skills of the child. It is performed with one hand, while the other fixes the massaged surface.
Massage movements are done from the fingertips to the forearm. The duration of the massage is 5 minutes. Massage is carried out daily or every other day (10-12 sessions per course).
The interval between massage courses for the development of fine motor skills in children can be from 10 to 30 days.
Necessary requirements for massage of the hands: the hands of the massage therapist must be clean, without decorations, the nails are short.
The hands of the person being massaged must also be clean. You can use baby cream or powder if your hands are sweaty. This is necessary for better sliding of the massage therapist's hands during the massage.
Preparatory exercises for fine motor skills before massage for children are as follows:
1. The child's hand lies freely on the table. An adult, fixing the wrist with one hand, with the other hand, alternately raises each finger of the baby to the maximum position.
2. The child's hand lies on the table with the palm surface up.
An adult holds the palm with one hand, the other bends the fingers inward.
So, the child is sitting, the hand lies freely on a hard flat surface (on the table).
Here is how hand massage is performed to develop fine motor skills in a child:
- the masseur with the whole palm produces a planar stroking of the back of the child's hand from the fingertips to the middle of the forearm. Repeat 3-5 times;
- the massage therapist performs a tong-like stroking separately of each finger of the child’s hand from the tips to the base of the finger;
- the massage therapist makes a tong-like circular rubbing of the fingers of the child's hand from the tip to the base of the finger;
- the massage therapist performs circular rubbing of the back and palmar surfaces of the hand from the base of the fingers to the wrist;
- repeats movement number 1;
- the massage therapist, using a hand or a vibrating massager, makes dotted movements of the back and palmar surfaces of the hand and fingers from the tips to the wrist;
- repeats movement number 1.
Proper coordination skills will be simply necessary in the later life of the baby, since in order to dress, draw, write and perform other activities, you need to make a lot of precise, coordinated movements. Massage and exercises for the development of fine motor skills in children can be performed to music or use poems and songs.
Games and exercises for the development of fine motor skills in children
How else can you develop fine motor skills in a child at home? An important place in the development of fine motor skills and coordination of movements of the hands and fingers is occupied by various exercises and games.
To stimulate fine motor skills, you can use the constructor.
It is better to start with large parts, gradually replacing them with smaller ones. Then move on to putting together puzzles, stringing beads, etc.
Examples of how to develop fine motor skills in a child of 4-5 years old:
1. Sprinkling any cereal from glass to glass. This exercise develops muscular hand coordination. When the child has mastered it, you can allow to pour or pour water or other drinks.
2. Tying knots. Teach your child how to make knots. It also develops coordination, fine motor skills and dexterity. You can start with a thick rope, then move on to a thinner one, such as a lace.
3. Opening and closing cans of various sizes. Place jars of different sizes, bottles, vials with lids in front of the child. Ask him to open all the lids and close them again. This lesson is also aimed at developing fine motor skills of the hands.
4. You can sew small bags and fill them, for example, with semolina, large pasta, rice, cotton wool, etc. Let the child feel these bags and guess what is in them.
This is not a complete range of games for the development of fine motor skills in children, coordination of hand and finger movements. Parents can supplement them with other exercises.
Skills of children 6-7 years old
 Primary school children should have basic hygiene skills. They are already quite independent and quite capable of self-service. They are able to brush their own teeth (under the supervision of adults), rinse their mouth after eating, wash their faces, take a shower or bath, dress and undress on their own, tie shoelaces, fasten buttons, and take care of their hair. Such skills are especially important, since at this age children begin to go to school, where their parents will no longer be around.
Primary school children should have basic hygiene skills. They are already quite independent and quite capable of self-service. They are able to brush their own teeth (under the supervision of adults), rinse their mouth after eating, wash their faces, take a shower or bath, dress and undress on their own, tie shoelaces, fasten buttons, and take care of their hair. Such skills are especially important, since at this age children begin to go to school, where their parents will no longer be around.
It is very important that younger students are taught to be neat. They must understand that rumpled, dirty things look bad, and sloppy hair and dirty nails make them ugly.
Children of primary school age must be Very often, parents seek to free the child from work duties and do everything for him that he could well do himself (for example, fold toys or clean up the desk). Children 6-7 years old who do not observe the daily routine, are not accustomed to work and do not have the skills to perform socially useful work, it can be very difficult in the school team. At school, they will definitely have new responsibilities: class duties, helping to prepare the class for the lesson and others with which they will have to cope on their own.
The article has been read 14,782 times.
Project "Development of fine motor skills in children of primary preschool age"
Educator: Yakovleva E.V.
Project type: educational, creative.
Project duration: long term.
By number of participants: group.
Project participants:
Children of the second younger group, educators, parents of pupils.
Relevance:
It is known that in recent years the level of speech development of children has decreased markedly. One of the reasons for this is that parents talk less to their children because of their busy schedule. Children themselves talk less because they watch more TV. They are less likely to do something with their own hands, because modern toys and things are designed as conveniently as possible, but not effective for the development of motor skills (clothes and shoes with Velcro instead of laces and buttons, books and manuals with stickers instead of pictures for cutting, etc. )
Today, everyone knows that finger games develop the child's brain, stimulate the development of speech, creativity, imagination of the baby, they can improve the pronunciation of many sounds. In general, the better the fingers and the whole hand work, the better the child speaks.
After all, it is the development of the hand that plays an important role in the formation of the brain and the formation of speech. And that is why the child's verbal speech begins when the movements of his fingers reach sufficient accuracy. The child's hands, as it were, prepare the ground for the subsequent development of speech.
The development of fine motor skills is also important because the entire future life of the child requires the use of precise, coordinated movements of the hands and fingers, which are necessary to dress, draw and write, as well as perform a variety of household and educational activities. That is why work on the development of fine motor skills must begin at an early age. In addition, fine motor skills interact with attention, imagination, thinking, memory and speech of the child.
This determined the theme of my future work "The development of fine motor skills in children of primary preschool age."
Target: purposeful work on the formation of fine movements of the fingers in order to develop active speech in children of primary preschool age.
Tasks:
1. use a variety of techniques and methods for the formation of fine finger movements in children of primary preschool age;
2.formation of practical skills of productive and speech activity
3. strengthening the physical and mental health of children;
4. development of cognitive mental processes: voluntary attention, visual and auditory perception, memory;
5. increasing the level of speech development of children;
6. education of moral qualities in relation to others (goodwill, camaraderie, etc.);
7. education and development of artistic taste;
8. involve parents in the implementation of the project.
Stage I - preparatory
1. Drawing up a long-term plan of project activities.
2. Selection of methodological, fiction, illustrative materials, didactic, finger, outdoor games, etc.
3. Identification of the level of development of fine motor skills in children.
4. Consultation for parents “The importance of fine motor skills in the development of speech in preschool children”.
5. Replenishment of the subject-developing environment of the younger group.
II stage - practical
1. Implementation of the developed system of work on the development of fine motor skills in children of primary preschool age.
2. Increasing the pedagogical competence of parents in the development of fine motor skills of children of the second younger group:
- Master class for parents "Development of fine motor skills of children
at home"
- Preparation of visual information and advisory material for parents
- Memo for parents: “We play with our fingers - we repeat verses! »
3. Open lesson, with a demonstration of the introduction of finger games in the course of the lesson
4. Monitoring the level of development of fine motor skills in children of the second younger group.
Stage III - final
1. Generalization of the results of work with children and parents.
2. Analysis of the effectiveness of the system of work on the development of fine motor skills of hands in children of primary preschool age
3.Creative self-presentation at the teachers' council on the success of the project
4. Exhibition of children's work using non-traditional methods
drawings and applications.
Expected results:
- the vocabulary of children will increase, the speech of children will become more emotional and expressive;
- the speech activity of children in various activities will increase;
- parents will become like-minded with teachers on the development of fine motor skills in working with children;
- parents will receive the necessary knowledge on this topic;
- the proposed games and exercises will help develop fine motor skills of children's hands;
- formation of self-service skills in accordance with age characteristics
- hands will acquire mobility, flexibility, stiffness of movements will disappear.
Project summary:
There is a positive trend in the development of fine motor skills of children's hands. Purposeful, systematic work on the development of fine motor skills of hands in preschool children contributes to:
- an increase in the vocabulary of children, the speech of children becomes more emotional and expressive;
- hands acquire mobility, flexibility, stiffness of movements disappears;
- maintaining the physical and mental health of the child.
The younger preschool age of a child is unique in its significance for speech development: during this period, the child has an increased sensitivity to language, its sound and semantic side.
Today, everyone, without exception, knows that finger games develop the child's brain, stimulate the development of speech, creativity, the baby's imagination, they can improve the pronunciation of many sounds. In general, the better the fingers and the whole hand work, the better the child speaks.
The fact is that the hand has the largest “representation” in the cerebral cortex, therefore it is the development of the hand that plays an important role in the formation of the brain and the development of speech. And that is why the child's verbal speech begins when the movements of his fingers reach sufficient accuracy. The child's hands, as it were, prepare the ground for the subsequent development of speech.
Finger games and exercises are a unique tool for the development of fine motor skills and speech in their unity and interconnection. Learning texts using "finger" gymnastics stimulates the development of speech, spatial thinking, attention, imagination, brings up the speed of reaction and emotional expressiveness.
A very important factor for the development of speech is that in finger games all imitative actions are accompanied by verses. Poems attract the attention of kids and are easy to remember.
While training the subtle movements of the fingers, I actively used not only the designs created from the fingers, in accordance with the proposed poetic text, but also various games and activities with objects: natural material, paper, plasticine, beads, lacing, counting sticks, matches , mosaic, designer, etc. She also used various types of theaters: shadow, finger, table, glove puppets. Such activities also contribute to the interaction of fine motor skills of the fingers with such higher mental processes as memory, attention, thinking, spatial perception, imagination, observation.
Taking into account the developing function of the object environment, which requires a combination of traditional and new components for its implementation, ensuring the continuity of the development of activities from its simple forms to more complex ones, the group is equipped with a “Center for the Development of Fine Motor Skills”.
To involve parents in the implementation of the project, I selected and designed visually - informational and advisory material for parents, held a parent meeting with the participation of a psychologist. At the parent meeting, a master class was held on the development of fine motor skills of the hands. Thanks to this, parents took an active part in the preparation of practical material and in consolidating the games being learned with children at home.
Thanks to the use of the accumulated material in practice, according to the results of a diagnostic examination, the pupils improve their speech skills, the level of visual skills has increased. And also, many children have noticeably increased self-esteem.
As a generalization of the work done, a presentation was presented at the pedagogical council on the topic: “Development of speech through finger games”.
Planning
Week 1Monday 15.02.
Finger game "Fingers say hello"
Games with a constructor
Tuesday 16.02.
Finger game "Goat"
Mosaic games
Wednesday 17.02.
Finger game "We cooked soup"
"Smoothing crumpled paper lumps from colored paper."
Thursday 18.02.
Finger game "Ship"
Working with coloring pages - hatching
Friday 19.02.
Finger game "Two funny geese"
Modeling from clay and plasticine
Saturday 20.02.
Finger game "Banka"
Hide the handkerchief
2 weeks
Wednesday 24.02.
Finger game "Family"
Looking for small toys in a bowl with lids
Thursday 25.02.
Finger game "Oh frost, frost ..."
Clothespin games
Friday 26.02.
Finger game "Orange"
Game with balls
3 week
Monday 29.02.
Finger game "I bake, bake, bake ..."
Rolling on the table, between the palms of pencils, balls, etc.
Tuesday 01.03.
Finger game "Finger Riddles"
Collecting puzzles and split pictures
Wednesday 02.03.
Finger game "House"
Paper tearing (by pinching off the sheet)
Thursday 03.03.
Finger game "Malania"
"Beads for mom" stringing
Friday 04.03.
Finger game "Gourmet"
Drawing with an unconventional method
4 week
Wednesday 09.03.
Finger game "We wash clothes"
Working with plasticine
Thursday 10.03.
Finger game "Wait a minute"
Finger gymnastics - lacing
Friday 11.03.
Finger game "Snow, snow"
Hand and finger massage
Synopsis of GCD. Theme "Visiting the Chanterelle".
Target: development of fine motor skills in preschool children.Tasks: - cognitive: to consolidate the idea of \u200b\u200bwild animals (bear, fox, hare, hedgehog, squirrel) - educational: learn to correlate the words of the poem with movements, imitate playing various instruments, imitate their sounds. To teach the ability to conduct a dialogue with the teacher: listen and understand the question asked, answer it clearly, speak at a normal pace. Continue to teach how to hold a pencil correctly, without straining your muscles and without squeezing your fingers tightly; to achieve a line with a pencil without lifting it from the paper, in the middle of the track.
-correctional and developmental: develop attention, memory of children, develop fine motor skills of hands. Teach children to grab small objects with their palms and carry them to another place. - educational: to form a benevolent attitude of children towards forest animals, a desire to help them. Raising a sense of collectivism.
- gaming: improve the ability to use games with small objects.
Material :
Demo: soft toys, Christmas trees. Dispensing: trays, nuts, bowls, baskets, pasta, small toys, split pictures, pencils, leaflets with the road, sweets.
Lesson progress:
The teacher with the children enter the group, greet.
caregiver: Children, look where we got to? (There are several Christmas trees)
Children: In the forest!
A bunny sits under the Christmas tree and cries. Children ask, "Why is the bunny crying?"
Bunny: “It's Chanterelle's birthday today, I brought her gifts and lost them. What am I to do now? How will I go without presents?”
caregiver: "Children, let's help the bunny find gifts for the fox."
There are bowls with small pasta on the table, small toys are hidden in them.
Children find toys and name them:
- I found the doll. Etc.
The toys found are given to the bunny.
caregiver: Guys! Do you want to know who else is going to visit Chanterelle for her birthday? I'll give you a riddle, and you try to guess.
Instead of a fur coat, only needles
Wolves are not afraid of him,
A prickly ball, legs are not visible
To call him of course .... (Hedgehog)
Here is the Hedgehog.
Guys, our Hedgehog loves to play. Do you want to play with him?
Finger game "Hedgehog"
caregiver: Guys, let's see who else is going to visit Chanterelle. I have pictures where our hero is drawn. Oh, look, my pictures have scattered, can you help me collect them?
Children in subgroups of 3 people collect cut pictures.
-Who did you get in the pictures? That's right, Mishka.
Mishka comes to visit, but he gets lost and does not know which path to follow. Let's help Misha find his way. To do this, you need to draw a pencil without lifting it from the paper in the middle of the track, straight to Chanterelle (there are three tracks on the sheet, you must select the path from Bear to Chanterelle).
Educator: Guys, what animals have we already met?
Children: Hare, Hedgehog, Bear.
caregiver: Where do they all live? Correctly in the woods, and are called?
Children: - Wild animals.
caregiver: And which of the wild animals do we still know? I'll prompt you:
Deftly jumping through the trees
And hides nuts in a hollow?
Children: Squirrel.
caregiver: A squirrel brings nuts to a fox as a gift. It is hard for her to carry a lot of nuts, the baskets are heavy. Let's help her.
The contents of the baskets are poured onto 2 trays. Children are divided into 2 teams. On a signal, the children transfer the nuts from the trays to the baskets.
caregiver: All the animals gathered to visit the fox and began to have fun.
Invites children to play musical instruments (imaginary) and dance with animals.
Speech with movements "I play the violin ..."
I play violin
"Tili-li, til-li"
Jumping animals in the meadow
"Tili-li, til-li"
on the harmonica I play "Ry-ry-ry"
Jumping animals in the meadow
"Ry-ry-ry"
I play "doo-doo-doo" on the pipe
Jumping animals in the meadow
"Doo-doo-doo"
And now on the drum
"Boom-boom-boom, tram-there-there"
All the animals have fled
bushes, bushes
caregiver: Guys, did you like to play and have fun with the animals visiting Chanterelle?..... You were so smart today, you helped the animals to come to Chanterelle for her birthday. So many good things have been done. And who remembers who we helped today? (children's answers). Foxy is very grateful to you for your help. She really enjoyed playing and having fun with you, and she wants to treat you with delicious sweets.
Card file of games for the development of fine motor skills:
"Rolling on the table, between the palms of pencils and balls"Purpose: to develop fine motor skills.
Children are given faceted pencils. The child places the pencil between the palms and rotates it from the base of the palms to the fingertips.
"Playing with plasticine"
To learn how to roll "balls and sausages" between the palms, to develop the ability to cut small pieces from large ones with a stack. To form coordination of movements, develop the ability to regulate the force of pressing the stack, hold it correctly, develop imagination.
"Find your soul mate"- split pictures
Learn to distinguish parts of an object and combine them into a whole, develop visual orientation, fine motor skills.
"Lacing"- learn to put the lace in the hole
To teach how to thread a lace into a hole according to imitation, a model, to develop purposefulness of actions and fine motor skills.
"Puzzles"
This is a puzzle picture, which must be assembled from separate pieces. Puzzles are wooden, cardboard, foam and plastic. You need to start with simple puzzles consisting of two to four parts, each of which depicts a recognizable part (leg, head, paw, half of a boat, plane, ball, etc.).
"Bead Games"
Equipment: beads, threads.
We string beads on strings, making decoration for the game. We string the beads in a certain order, alternating in shape, color, or size.
"Mosaic work"
Equipment: mosaics of various types, samples of laid out figures.
Lay out several rows of plates of the same color. Lay out a picture from a mosaic, having a sample in front of your eyes. Make up your own drawing based on past experience.
"Games with the designer"
Constructor is a universal educational game. For kids, wooden and plastic constructors are suitable, with small details that are convenient to hold in your hands and apply or connect to each other.
"Games-with-magnets"
Games with magnets for children of the second year of life basically boil down to attaching figurines on magnets to different surfaces: a refrigerator, a magnetic board, metal objects (a mug, a battery, a saucepan, etc.) or to each other.
"Peg Games"
We attach clothespins to various objects: to a plastic bucket, to a wooden stick, to a book, to cardboard silhouettes (hedgehog, sun, flower, Christmas tree, etc.), to a rope, to fabric, etc.
"Games with paper and napkins"
Paper Snowballs: Show your child how to crumple up a piece of paper (or napkin) to make a snowball.
Paper snowflakes: Invite your child to tear a sheet of white paper (or napkin) into small pieces - these will be snowflakes.
Secrets: Wrap the toy in wrapping paper or foil and invite the baby to unwrap the gift.
"Finger Pool"
The child lowers his hands into a vessel with a homogeneous filler (water, sand, various cereals, any small objects) and mixes the contents for 5-10 minutes. Then the adult offers a vessel with a filler of a different texture. After several tests, the child, with his eyes closed, lowers his hands into the vessel and tries to guess its contents, without feeling its individual elements with his fingers.
"Drawing on the croup"
An adult takes a bright tray and scatters any cereal on it in a thin even layer. Runs the child's finger over the croup. Get a bright contrasting line. Then he invites the kid to draw a few arbitrary lines himself. You can draw together some objects (fence, rain, waves), letters.
"Hide the handkerchief"
The child crumples, starting from the corner, a handkerchief (or a plastic bag) so that it fits entirely in the fist.
All mothers know that children need to develop fine motor skills of their hands. But not everyone knows how to do it correctly, and indeed what is fine motor skills and what features does it have? What activities, games and exercises should be done with children to develop motor skills? Fine motor skills have a very important feature. It is associated with the nervous system, vision, attention, memory and perception of the child. Also, scientists have proven that the development of fine motor skills and the development of speech are very closely related. Therefore, for the timely development of the child's speech, it is necessary to pay great attention to the development of fine motor skills. Fine motor skills directly affect manual dexterity, handwriting, which will be formed in the future, and the reaction speed of the child.
Download:
Preview:
The development of fine motor skills in children.
All mothers know that children need to develop fine motor skills of their hands. But not everyone knows how to do it correctly, and indeed what is fine motor skills and what features does it have? What activities, games and exercises should be done with children to develop motor skills?
Fine motor skills are the ability to perform small and precise movements with the hands and fingers and toes as a result of the coordinated actions of the most important systems: nervous, muscular and bone. With regard to the motor skills of the hands and fingers, the term dexterity is often used. The fine motor area includes a wide variety of movements, from simple gestures (such as grasping a toy) to very complex movements (such as writing and drawing).
Fine motor skills have a very important feature. It is associated with the nervous system, vision, attention, memory and perception of the child. Also, scientists have proven that the development of fine motor skills and the development of speech are very closely related. And this is explained very simply. In the brain, speech and motor centers are located very close to each other. Therefore, when the motor skills of the fingers are stimulated, the speech center begins to activate. That is why for the timely development of the child's speech, great attention must be paid to the development of fine motor skills. Fine motor skills directly affect manual dexterity, the emphasis that will be formed in the future, and the speed of the child's reaction.
Activities, games and exercises for the development of fine motor skills
beads
Children like to touch small objects, which is very useful. Therefore, you can put on some beads with beads of various sizes and shapes. The child will touch them with his fingers with joy and interest.
Bowl inserts.
From them you can build towers, put them into each other. This game develops the child's concept of the size of objects.
Cereals.
Pour any cereal into a bowl and give it to the baby. He will touch the cereal with his hand or spill it through his fingers. This game develops fine motor skills and tactile sensations well.
Jars with cereals.
Pour different cereals into jars and let the child dip his hand into each of the jars in turn. So he can feel different grains and take them with his fingers. You can complicate the task. In front of the child, bury some small object in the cereal and give him a jar. Let him try to find this item.
Drawing on the sand.
Pour sand onto the tray. Take the child's finger in your hand and run it across the sand. You can start with simple shapes - lines, a rectangle, a circle, gradually complicating the task.
Toys for the development of fine motor skills
Pea.
You will need a pea and a jar with a removable lid. Show the child that you first need to remove the lid, then take the pea with your fingers and put it in a jar, then close the lid. Ask your child to do the same. Don't be discouraged if it doesn't work the first time. Show the baby the whole chain of actions slowly several times, and then he will definitely be able to repeat everything. Active children quickly get bored with this game, in this case there is no need to force them. Offer the child a different game.
Screwing caps.
Such a simple activity as screwing and unscrewing the lids of cans, bottles, bubbles develops finger dexterity. Offer your baby vessels of different sizes and shapes, this will make the game more diverse.
Fastening, unfastening and lacing.
This exercise does not require any additional toys. Gradually include the child in the process of dressing. Let him fasten and unbutton his own buttons and zippers. This will not only develop hand movements, but also teach the child to be independent. Also, give your child some unnecessary lace-up shoes that will be a great hand trainer.
Modeling.
Modeling is suitable for children of all ages. Plasticine, clay, dough are suitable for modeling. When you are going to bake something, be sure to bring your child with you. He will love to knead and roll out the dough. In addition, he will be proud that he helps his mother.
Exercises for the development of fine motor skills of hands
Drawing and coloring.
It is very useful to trace the outline of pictures, consisting of dotted lines, as well as color objects of various shapes. It is very useful to draw on vertical surfaces: wall, blackboard, mirror. Therefore, it is advisable to hang a special board for the baby so that he draws.
Collecting mosaics and puzzles.
For children 3 years old, puzzles and mosaics with large parts are chosen. Puzzles also train the imagination.
Cutting out.
Buy baby scissors, glue stick, colored paper and cardboard. Teach him to craft. Cut out pictures, paste them, make snowflakes, etc. This will not only develop fine motor skills, but also spatial imagination and creative thinking.
However, it is worth remembering one simple thing. Games for the development of fine motor skills should be carried out under the supervision of adults. Otherwise, the child may swallow some small part or choke on it. You need to play games and perform exercises that develop fine motor skills systematically. Practice with your child every day and you will soon notice that your baby's movements become more and more smooth, clear and coordinated each time.
The development of fine motor skills of hands in young children, the preschool period, occupies the minds of parents who are concerned about the future education of the child at school. In our article, you will learn what fine motor skills are, how and why to develop them.
Definition
M. Montessori, V.A. Sukhomlinsky, A.R. Luria, other psychologists, teachers and physiologists devoted their lives to studying the properties and characteristics of fine motor skills. They found the dependence of the level of speech development of preschoolers on the organization of movements with fingers and hands. The accuracy of the manipulation depends on the development of small muscles. When fastening buttons, drawing, sculpting, the work of the speech departments of the brain is enhanced.
Fine motor skills of the hands are connected with consciousness, thinking, spatial orientation, memory, and vision. This is also important for the development of speech, success in teaching a child, and the future life of an adult.
Thus, under the concept of the speech therapy term “fine motor skills of the hands” means a complex of mental and physiological processes. Visual, bone, muscular, nervous systems are involved. The accuracy, perfection of the motor skills of the fingers and the speed of development of the speech function depend on the coherence of their interaction.
Diagnostics
An examination of the level of development of the physiological characteristics of fine motor skills in children is an important stage in corrective, developmental work.
Diagnosis is carried out by speech therapists, defectologists, neurologists, kindergarten teachers.
The peculiarity of the survey is that the child repeats the manipulations after the teacher. For the lesson, create a relaxed atmosphere, it is better to use the game. Tasks are divided according to the age of the subjects.
To examine the development of fine motor skills of hands in children 3-4 years old, the following exercises are used:
- Touching with index fingers to the nose with closed eyes.
- Flexion of the phalanges on both hands alternately.
- Performing two opposite actions at the same time. For example, one hand is clenched into a fist, while the fingers of the other are unclenched.
- Folding the thumb and forefinger into a ring.
- Manipulations with buttons: unbuttoning, fastening.
- Transferring small items from the table to the box.

An analysis of the level of development of fine motor skills of hands in children 4-5 years old is carried out as follows:
- The child must draw a straight, broken line.
- String buttons on a thread.
- Extend your index and middle fingers.
- Stroke all other fingers with your thumb.
- Cut paper into even strips.
- Perform a pinch movement and straighten the palm back freely.
Norms
The development of fine motor skills in children occurs gradually. By a certain age, the child must perform the following set of actions, corresponding to the level of physiological, mental development:
- At 2-2.5 years old, the baby knows how to unfasten Velcro, large buttons, pushes small objects into holes, removes clothespins, draws in a sweeping manner. Masters simple exercises of finger gymnastics.
- At 2.5 - 3 years old, he unscrews the lids, draws with his fingers, sculpts cakes, copies the lines. He knows how to string beads on a hard thread, wire, cut a sheet of paper, collect cereals with a spoon in a container and transfer it to another jar.
- At 3-3.5 years old, he draws straight lines, outlines dotted lines, repeats simple figures according to the model with a pencil, sculpts balls, plasticine sausages. He knows how to fasten and unfasten all types of locks, buttons, performs finger gymnastics well, is fluent in scissors.
- At 4 years old, he holds a pencil correctly, draws hexagons, stars, cuts out any geometric shapes. He knows how to sort small objects, unfolds wrappers, strings small beads on a thread, sculpts figures from dough, plasticine, ties knots, repeats the contours of objects with his finger in the air.
- At the age of 5, he copies letters, numbers, folds paper several times, draws a house. Able to identify small objects by touch, lace up shoes, catch the ball with two handles. At the senior preschool age, the skills of developing fine motor skills in children lie in the fact that hands and fingers are already formed to master writing.
- At the age of 6, a preschooler copies complex figures with a pencil, parts of a person’s body, catches a thrown object with one hand, and can perform a mirror image. He knows how to play the keyboard instrument, braids pigtails, almost completely masters the possibilities of hand motor skills by grade 1.
The development of skills in children 2-3 years old can take place individually, with slight deviations. Most often, they quickly catch up with their peers. If strong deviations from the norm are detected in the diagnostics, for example, 1-2 tasks out of 6 are performed correctly or moderately, we can talk about violations in the intellectual, physiological terms. Correction of development is carried out by specialists, most often one year of full-fledged classes with a teacher is enough for children to enter the age norm, to eliminate lags in the development of speech.
If by the age of 3-4 the baby cannot hold a pencil correctly, does not fold a pyramid, does not hold a spoon, scissors in his hand, does not catch, does not throw a ball, then you need to urgently contact a specialist. These indicators indicate serious deviations in development and upbringing.

We develop fine motor skills
For preschool children, the following activities are used.
Massage
Self-massage and adult assistance are used. Spend 2 times a day, use as a warm-up before drawing, sculpting. The set of exercises includes:
- Kneading of palms, brushes.
- Immersion of the palms in a dry pool with sand, grits, plastic bottle caps, etc.
- Use of devices: hedgehogs, finger rings, marlbs balls.
Massage of the palms should be done with elastic movements, rub the skin until red. You can use improvised means, for example, a pencil, nuts. In the first lesson, teach the preschoolers the correct massaging movements, so that he could apply the necessary amount of strength to knead his hands.
The nut rolls between the palms, is held along the edges by weight. The pencil is inserted between the fingers, fixed in a certain position.

For kids aged 3-5 years, the following self-massage exercises are suitable:
- Pin
The fingertips are kneaded with a clothespin. The skin is bitten with light, but tangible movements. The clothespin seems to bite. Be sure to carry out the procedure on both handles. - Warm-up with Su-Jok
These are special balls with spikes for the development of fine motor skills of the hands. Exercise improves blood flow, kneads and trains muscles.
Children roll them on their palms from top to bottom.

It is important not to forget about health protection, the skin of hands and fingers should be clean, without scratches, prepared for massage.
finger games
Necessary for the development of speech and coordination of movements, warming up the muscles of the palms, phalanges.
- legs
Fingers make stepping movements on the table

Children use their fingers to make glasses, forming circles with the thumb and forefinger. Bring them to your eyes.

- Let's go for mushrooms
We count fingers: one, two, three, etc. We bend each finger in turn, saying a rhyme about how the fingers were looking for mushrooms, we do not unclench the cam.

- Chair and table
We depict a table with a fist and a palm, change the position of the hands one by one. Then a chair: bring an open palm to the fist, put it on one side of the fist.

- boat
Verse used:
The fox cub swims in a boat (palms are folded in the form of a boat),
The hare calls into the boat (the kids wave, calling for a friend).

- Scissors
The child depicts scissors with his fingers, makes characteristic movements, as if cutting the fabric.

Finger paint
The development of fine motor skills occurs faster through visual activity. Use modern methods and materials for drawing. One of them is finger paints.
Draw figures, landscapes, large compositions based on a model or fantasy.
With a child 1-2 years old, draw lines, circles. With children from 3-4 years old - animals, houses, cars, geometric shapes.

To work with older preschoolers, print out complex patterns for drawings, with the need to use a large number of shades, with an image of polygons, numbers, letters.












Application
A fun activity for kids of all ages. Children from 4-5 years old already cut out figures of large and small sizes. They know how to stick paper to cardboard, place the elements of the work on the sheet.
Use designs with small details for appliqués. For example, an autumn tree with many small leaves on the crown, or an applique in the shape of a fish, where you need to cut each scale separately.

As a material, colored paper, napkins, corrugated cardboard, natural remedies (sticks, pebbles, sand, cereals) are suitable.

Rolled napkins make great flowers. The material can not only be twisted into balls, but also torn into pieces, gluing the pieces on top of each other.

You can make a sheep out of colored rice and semolina. The contour of a sheep is drawn on the sheet, it is covered with PVA glue, then semolina is sprinkled on the body, and the legs and horns are made of rice.
modeling
For classes, plasticine of various hardness, dough, kinetic sand are used.
Soft plasticine is suitable for kids aged 2-4 years. They need to be taught to roll sausages, balls, design simple shapes by attaching them to cardboard.

Older children can already perform complex tasks. For example, a picture from plasticine in different ways.

Use the smudge and build method. Be sure to clearly show the child how the parts are connected, how to make small parts and use colored elements.




During classes, not only motor skills develop, but also the creative potential of the child, the horizons expand, knowledge about the color, shape, size, texture of the material. Visual activity develops the skill of perseverance, purposefulness.
How to conduct classes
- Work with your child regularly, paying attention to massage, games, gymnastics, and creative activities.
- At 2-3 years old, it is enough to massage the hands and fingers for 3-5 minutes. Then perform 1-2 exercises of gymnastics with the pronunciation of small rhymes. A couple of times a week, hold classes in modeling, learning to draw.
- By the age of 4-5, increase the time of self-massage to 10-15 minutes 2 times a day. Do finger exercises for at least 20 minutes a day. The child should draw or sculpt daily.
- In the senior preschool period, you can study for more than 30 minutes without a break. Alternate massage, finger and hand training in one session. Sculpt, draw with your child together, be sure to include complex elements in the composition, the image of letters and numbers.
- The main principle of classes is systematic, consistency. Consider the developmental features of children when selecting materials, cards, poems, tasks.
In kindergarten there are stands, guidelines for parents on how to develop fine motor skills in a child. Consult with teachers and repeat the material covered in the preschool educational institution at home.
The development of fine motor skills in children 3-4 years old
In Russia, it has long been customary to teach a child to play with his fingers from an early age. These were such games as “Ladushki”, “Forty-white-sided”, etc. After washing the baby’s hands, they wiped them with a towel, as if massaging each finger individually.
It has been proven that fine work with fingers contributes to the development of speech in children. Therefore, it is very important to develop fine motor skills in a child from a very early age. But just doing the exercises will be boring for the baby - you need to turn them into interesting and useful games.
fine motor skills - coordinated movements of the small muscles of the fingers and hands. They are important not only for performing various daily activities, but also for stimulating the development of the child's brain.
Along with the development of fine motor skills, memory, attention, and vocabulary of your baby develop.
Children aged 3-4 years are already capable of learning, however, any new information should be presented to them in an accessible game form. To develop motor skills, teachers recommend paying attention to the following types of gaming activities:
1. "Cones on a plate"
Invite your child to roll pine, spruce, and cedar cones on a plate. First let him roll one bump, then two, three, etc.
2. Circle the object
You can circle everything that comes to hand: the bottom of a glass, an inverted saucer, your own palm, a spoon, etc.
3. "Magic pattern"
Poke holes in thick cardboard with an awl or nail - they should be arranged in a certain order and represent a geometric figure, pattern or pattern. Let the kid independently embroider a pattern with a thick needle with a bright thread.
4. "Sew on a button"
Show your child how to sew on a button. After that, let the baby do the same under your supervision.
5. "Colorful snowflakes"
Show your child how to make paper snowflakes. Once your child is able to cut out the snowflake, ask him to color it. Let the child cut out a few more snowflakes and color them as well.
6. "Lace up your shoe"
Show your child how to lace up a boot in different ways. First, lace up the boot with it. Once your toddler has mastered the lacing technique, ask him to lace up the boot himself.
7. "Magic pipette"
Invite your child to play wizard. On a piece of paper, paint a few multi-colored spots with paints. Show your child how to use the dropper to drop only one drop. After that, let him drop a drop of water on each colored spot. Then watch with your child how the spot will grow and turn into a pattern.
8. "Little Apothecary"
Tell your child about the work of a pharmacist. Then show him how to use tweezers to lay out and shift the beads from place to place. In the game, you can use beads of different sizes.
finger games
A very important part of the development of fine motor skills are finger games that activate the child's brain, contribute to the development of speech and help prepare the hand for writing.
During these games, children develop dexterity, the ability to control their actions and concentrate on one type of activity.
By the age of 5, children are already learning to perform tasks that require sufficient accuracy and coordination of hand movements.
All the exercises suggested here should be performed at a slow pace, 3 to 5 times, first with one and then with the other hand. Make sure they are done correctly. Do the exercises for a few minutes, 2-3 times a day.
1. "Kitten"
Squeeze and unclench the fingers of both hands.
You, kitten, are not food!
You better look for your mom.
2. "Squirrel"
Unbend all fingers one by one, starting with the thumb. First do the exercise with your right hand, and then with your left.
A squirrel sits on a cart
She sells nuts
fox-sister,
Sparrow, titmouse,
Bear fat-fifth,
Mustachioed hare.
3. "Tsap-scratch"
The child puts his hand on top of yours. You read a poem, and the baby listens attentively to you. At the words “tac-scratch”, he must pull back the handle so that his fingers do not fall into your “trap”. Then the other hand comes into play. After a while, you can switch roles.
On the palm, on the path
Little cat walks
In small paws
Hid the scratches.
If you suddenly want
Sharpens claws.
Tsap-scratch!
4. "Funny fingers"
Clench your fingers into a fist. Unbend them one by one, starting with the big one. Then turn the brush to the right and left 5 times.
Thumb - danced,
Index - jumped,
Middle finger - squatted
Nameless - everything was spinning,
And the little finger was having fun.
5. "Fan"
Keep your palms in front of you, fingers pressed ("fan closed"). Spread widely, and then press your fingers together (“open and close the fan”). Wave your brushes towards you and away from you (“fanning”) 6-8 times.
6. "Peacock"
Attach all fingers of the left hand to the thumb. Place the palm of your right hand with open fingers on the back of your left hand ("peacock's tail"). Connect and spread your fingers ("peacock opens and closes the tail").

At the cheerful peacock
Fruit basket full.
A peacock is waiting for friends to visit,
For now, there is only one peacock.
7. "Butterfly"
Clench your fingers into a fist. Alternately straighten the little finger, ring and middle fingers, and connect the thumb and forefinger into a ring. With straightened fingers, make quick movements (“the butterfly flaps its wings”) - first with one, then with the other hand.
8. “Stand up for exercises! »
Bend your fingers to the palm one by one, starting with the little finger. Then with your thumb touch all the others, as if raising them to charge. After that, do exercises - squeeze and unclench the fist 5 times.
Fifth finger - fast asleep.
The fourth finger - only dozed off.
The third finger - fell asleep.
The second finger - all yawned.
The first finger stood up cheerfully,
Picked up everyone.
Playing musical instruments perfectly develops fine motor skills of the hands, and also has a positive effect on the thinking processes of the baby. If you did not plan to teach your child music at such an early age, buy him a toy instrument (synthesizer, guitar, flute), the mastery of which will improve the child's motor skills.
In addition, fine motor skills can be developed with the help of other creative activities - drawing, sewing, clay modeling, dough or kinetic sand.