Hemorrhagic enanthema on the soft palate. Petechiae. Petechiae in a child
Petechiae are flat, as well as dotted spots of a rounded shape, saturated red, reaching sizes in diameter of 1-2 millimeters. Petechiae are not found on palpation and do not protrude above the skin surface. Their size varies from a point to a pea. Home distinctive feature petechiae from flea bites is the lack of a central point.
Commitment completed in 36 hours, palms and plants respected. This is diffuse erythema, bleached with pressure, there are numerous dotted papular elevations of 1-2 mm. In the body, erythema is noted in the folds of the skin of the inguinal, shelter, ulnar ante and abdominal cavity and pressure points. In the cubital fossa and catch shelters, a linear petechial character of the eruption is visible. Vesicular lesions on the head may appear in the abdomen and chest.
IN best case the rash is a fuzzy, scarlet color. Although adult scarlet fever is not as common as 6 months to 10 years of age, it is still helpful to know about it, as it is a highly contagious disease. If a household member has this, it can be distributed immediately, especially to those listed in age group. Therefore, you should be aware of the symptoms to be aware of so that if they show up, you will know what to do so as not to make the situation worse and prevent others from getting hurt.
Petechiae on the skin at first have a pronounced bright red color, turning into dark brown. After a while, they lose their brightness, turn pale and disappear, only sometimes, after themselves, leaving a small pigment spot.
Petechiae causes
Their occurrence is associated with small capillary hemorrhages (small hemorrhages) in the skin, as well as the mucous membrane.
The following symptoms are commonly present in adult scarlet fever. Red rashes that usually appear two to five days after the onset of the sore throat and fever. Eruptions will look like a tan and with texture like texture sandpaper. Strawberry tongue, or a condition in which the tongue looks red and bumpy and is surrounded by a white coating that can be compared to said fruit. This is one of the most obvious indicators of the presence of scarlet fever. Dark areas can form in areas such as the armpits, knees, groin, neck, and elbows. Redness of the face due to the presence of eruptions A sore throat can lead to conditions such as difficulty swallowing. The presence of swollen lymph nodes that are tender to the touch. Nausea, headache and vomiting may also occur, as well as other symptoms.
- Fever that can reach over 38.3 degrees Celsius.
- Sore throat caused by bacteria.
The causes of petechiae are physical injuries. As an example, this swipe over the skin.
Petechiae on the skin occur in all age categories(Children Adults). TO rare reasons the occurrence of petichia on the face include coughing, an attack of vomiting, leading to the appearance of capillary ruptures near the eyes. Such manifestations are characteristic of children.
It all starts with a sore throat and fever, and a few days after the rash appears, there are signs that the disease is no longer contagious. That is why, even if you are only in the fever stage, you should already distance yourself from the children at home, so no matter how it develops, you are saved.
Adult scarlet fever is diagnosed after a plaster test. When its existence is determined, antibiotics will be given to kill the bacteria that cause the disease. Remember to take your medicine before last day prescription to ensure bacteria are removed to avoid further complications. It is better not to allow it to spread, and not the whole world to endure the same.
Petechiae can appear after pressure is applied to skin tissue. These hemorrhages disappear after a few days on their own and are not dangerous.
Petechiae on the skin can be manifestations of thrombocytopenia, which occurs when the number of platelets in the blood decreases. This condition can occur after taking medications, as well as in the presence of an infection in the body. Violation of the function of blood clotting can also lead to petechiae. There are times when capillaries break after taking certain medications.
The best defense you can have against pollution is to know a lot of scarlet information. Don't let your children suffer to protect them by learning more about scarlet fever. They are caused by enteroviruses - small RNA viruses. It is transmitted by the fecal-oral route, which means that the infection is spread through the entrance to the mouth. healthy person from virus-infected fecal particles.
Viruses are highly contagious and spread easily among young children, especially in schools and kindergartens. The illness occurs from 2-3 days to a week, with onset having the flu. The child has a poor general condition, relaxation, loss of appetite and refusal to drink fluids.
The list of diseases in which petechiae appears:, rheumatoid, Wegener's granulomatosis, infective endocarditis, scurvy, periarteritis nodosa, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, hypercorticism, purpura, typhoid fever, werlhof disease, smallpox, septicemia.
Primary petechiae on the skin are distinguished, in which the formations persist for up to several days. Over time, their outlines turn into less bright ones, and the brightness of the spot itself fades. Further, the primary petechiae on the skin turn dark and sometimes become a greenish-yellow hue. Sometimes there are cases of the appearance of barely noticeable vesicles above the spots, filled with liquid and having a purulent character, but this nature of the disease occurs with recurrent fever.
Typical is vomiting and involuntary leakage of saliva from the mouth in infants. A typical vesicular rash appears on the back of the throat, tonsils, and soft palate. The bubbles are filled with clear content. After cracking, small wounds are formed, ulcers up to 5 millimeters in size, which are easily and quickly cured without the formation of sticks. Butts at the back of the mouth and throat begin to appear about 2 days after initial symptoms. Ulcers usually have grey colour and often the rash is surrounded by a red rampart.
Wounds usually disappear in about 7 days. Enlarged and painful underlying and cervical lymph nodes were found. External rashes can occur on the skin of the body without a specific localization. They usually do not itch and change quickly. Laboratory tests in typical herpanglin are not required.
Primary petechiae, in comparison, are smaller than roseolous spots and occur in small numbers. Many patients confuse primary petechiae with insect bites. But it is enough to study the spots under a microscope to understand that this is not so. Hemorrhage is observed immediately, however rapid disappearance makes it impossible to take into account this symptom.
Complications with herpanginal are very rare. Warning signs- dizziness, symptoms of dehydration - dry mouth, drowsiness, decreased frequency of urination, dark-colored urine or sunken eyes, severe deterioration general condition requiring a doctor's review.
Treatment is based on various factors such as the child's age, specific symptoms, and tolerance to certain medicines. At viral infections antibiotics are not effective drug. The main goal of treatment is to limit and control symptoms.
Secondary petechiae on the skin often result in leakage of blood pigment into the surrounding tissue itself. Secondary petechiae are characterized by non-disappearance on pressure. For roseolous spots, the transition to secondary petechiae is always characteristic.
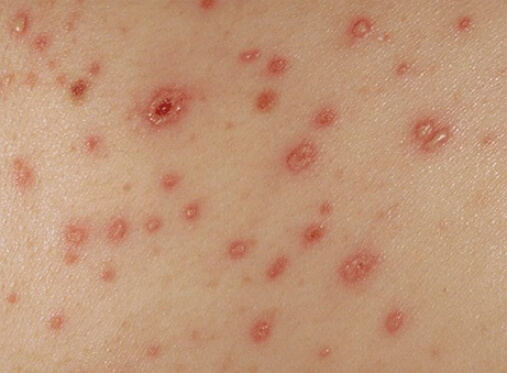
photo of petechiae on baby's skin
Prescribing fever-lowering drugs such as paracetamol and ibuprofen, which act as an analgesic. Aspirin is not given to children under the age of 16 as Ray's syndrome can develop. No antibiotics are prescribed unless additional bacterial infection. Local anesthetics are used to relieve mouth pain, although they are not usually needed. Increase your child's fluid intake. Any cold dairy products are acceptable. Avoid giving spicy, fried or acid foods.
Symptoms of herpangina usually disappear within about 7 days without lasting effects for the health of the child. Spring and autumn are the seasons of drawing. What do we know about the most common of them - scarlet fever and chickenpox? Scarlet fever is an infection caused by streptococci - most often in young children. The first symptoms are called the triad. These include fever, throat, and vomiting.
Petechiae in a child
The disease in a baby is represented by small, rounded subcutaneous blood spots that occur after a rupture. blood vessels, as well as leakage of blood under the very surface of the skin or mucous membranes. The subcutaneous layer of petechiae is struck pointwise, and their diameter reaches up to 1-2 mm. A feature of these formations is the coverage of a fairly large area of the skin and mucous membranes. The eruptions give the impression of flat spots and do not change their color even when pressed. Petechiae appear on all kinds of skin areas, including the oral cavity.
The main symptom of scarlet fever is a very severe rash of small red spots, which is caused by a toxin released from the hemolytic streptococcal infection. Under pressure on the skin, the eruption becomes pale - this is a sign of a scarlet fever rash. The rash is more intense than inner part hands and feet, especially in the folds of the body. The rash is not only on the nose and around the mouth, the pale Filatov-Koplik triangle. The patient's face has a distinct appearance - the cheeks are bright red, without a rash on them, and a pale triangle appears around the nose and mouth.
Petechiae in children causes
One of the main causes of the disease in children is trauma, as well as damage to the capillaries, after which their rupture occurs, as well as blood leakage, which spreads into the subcutaneous surface.
Petechiae in children occur during play, and the causes are accidental falls. The disease can occur with septicemia - this is an infection of the blood, due to the ingress of pathogenic bacteria. Septicemia occurs against the background of any disease. Babies often suffer early age, because their immunity is not sufficiently formed to hold the pathological process.
Another feature of scarlet fever is that the rash is present in the oral cavity. The color of the tongue changes - under the influence of the toxin, it becomes dark red with visible tips - the so-called "raspberry tongue". A soft rash appears on the soft palate. You can also develop purulent angina with a sharp increase in temperature, sore throat and swollen lymph nodes.
Scarlet fever can cause some complications and therefore it is very important to have timely recognition and effective treatment this disease. Early Complications scarlet fever includes lymphadenitis, otitis, and sinusitis, while the joints, kidneys, liver, heart, and brain may be damaged in the latter.
Petechiae in the sky appear due to trauma at the time of eating solid food. bad care for the baby and malnutrition can provoke childhood scurvy, which is characterized by scattered petechial hemorrhage of the skin, as well as the oral mucosa. Causes of hemorrhage skin in children it is a lack of vitamin K.
Treatment of scarlet fever is very effective with penicillin-based drugs, which are less sensitive to streptococci. Antibiotics from the group of penicillin and cephalosporins are used for 7-10 days. When antibiotics are administered, the use of a probiotic is also prescribed, as well as the consumption of many fluids to reduce the effects of toxins on the body.
However, according to experts, scarlet fever is not associated with acute infectious diseases. While chickenpox is an extremely contagious smallpox. Anyone who has not been exposed to chickenpox is infected and sick. Varicella begins with fever and rash. The most common symptom of this pattern is a blister. This rash is on the hair, mucous membranes and skin. The most intense is on the body and more deficient on the limbs.
Petechiae in children and their symptoms: heat, shortness of breath, rapid pulse, development of pulmonary insufficiency and fever. Toxic substances produced by microbes injure blood vessels and cause the formation of a rash, which is called hemorrhagic. With septicemia, the rash grows during the day. Severe course is accompanied by fainting and delusional states. The development of septicemia is very fast and its timely diagnosis and treatment are necessary conditions saving a child's life.
The varicella is called another leaflet because rabbit units are grain-sized and retain that size. It is important to know that the chickenpox rash is very itchy, and several bumps occur after a few days. Severely itchy kidneys can be treated with menthol, which cools and relieves itching, and the dried crust of the kidneys should remain free of infection because they can leave scars.
It is extremely important to know that chickenpox is very dangerous for people who are immunosuppressed in the elderly in patients taking corticosteroids or certain immunosuppressive therapies. It is also dangerous for pregnant women, especially in the first and last trimester pregnancy.
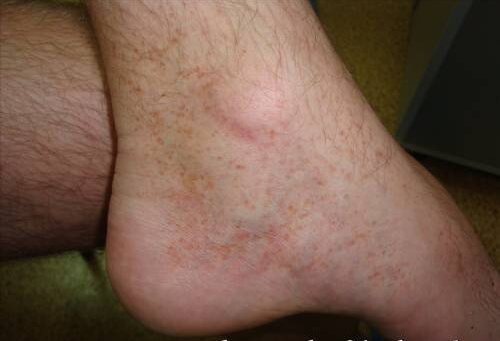
photo of petechiae on legs
Petechiae treatment
To solve this cosmetic problem resort to a surgical method.
Treatment of petechiae in children includes taking vitamins C, P, K, as well as liver extracts and blood transfusions, red blood cells, and the introduction of globulins. The fight against pathogenic bacteria includes the introduction of very strong antibiotics intravenously to the child. Provided that an infected wound or an infectious abscess caused septicemia, then surgical intervention is used.
Petechiae in a child
There is a vaccine against chickenpox, but, unfortunately, it is not yet available - in our neighbors Greece and Serbia, however, it is used. Manifestation of connective tissue and oral skin. Oral cavity is a particularly important diagnostic site because it can detect a number of diseases that can affect the health of the whole body. The oral cavity is easily accessible for non-invasive diagnostic purposes, so it should always be carefully monitored not only by the dentist, but also by other specialists.
With endocarditis, petechiae in children occur on the conjunctiva, as well as the trunk, buccal mucosa, distal extremities, and nail hemorrhages. Babies are worried about chills, sweating, fever, shortness of breath, pain in the heart. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital. The use of antibacterial drugs is fundamental, given the sensitivity of microbes to them. Infection with fungi is treated with Amphotericin with Fluconazole, taking into account the age dose.
C) The student must be aware of
At this stage, you most often notice changes in connective tissue and skin conditions, often systemic, so be sure to keep regular dental check-ups in mind so you can spot symptoms that are worrying, so you can get treatment quickly if needed.
Lichen - chronic inflammatory disease skin and mucous membranes, which sometimes occurs only in the mouth. Lichen planus can also appear on the tongue and is usually seen as a change in the plates. Lichens on red and white varieties are also common, red damage is erosion or fading, and depending on this, erosion and erosion can be distinguished. The gums may also be covered with lichen planus, followed by exfoliation. Irritable bowel syndrome may not present at all, or may present as a result of pain and burning, especially in response to hot and highly spiced foods, especially in the case of bipolar toffee.
Treatment of petechiae in children includes monitoring of serum biochemistry, as well as heart rate and monitoring of blood pressure readings.
In cases scarlet fever the mucous membrane of the soft palate is brightly hyperemic ("flaming"), angina is pronounced. After cleansing from plaque, usually on the 3-4th day from the onset of the disease, the tongue becomes "raspberry". Characterized by a pale nasolabial triangle on a hyperemic face, a small punctate rash on the body, lamellar peeling on the palms and soles.
IN Lately in connection with weakening of sanitary control, especially in commercial public catering establishments and in case of gross violation of elementary hygiene, food poisoning infections of streptococcal etiology have become more frequent. They differ, in addition to the development of acute gastroenteritis, which occurs with abdominal pain, sore throat, aggravated by swallowing, changes in the pharynx, you can see hyperemia, swelling of the mucous membranes, tonsillitis. Often these diseases are of a group nature and sometimes are characterized by a severe fulminant septic course with a fatal outcome. .
At rotavirus infection , in addition to acute and sometimes rapidly developing gastroenteritis, often beginning with diarrhea and subsequent vomiting, there are also very characteristic changes in the oropharynx. Its mucous membrane is hyperemic, the tongue is edematous. On the soft palate graininess, sometimes enanthema. Clinical picture in rotavirus infection is generally similar to that in other acute intestinal infections(cholera, salmonellosis, escherichiosis), but with them there are no changes in the oropharynx.
At some viral infections on the mucous membrane of the soft palate and back wall pharynx possible petechial rashes (hemorrhagic fevers, severe forms viral hepatitis). These changes are usually combined with universal hemorrhagic syndrome (DIC). Various lesions of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx - petechial, herpetic, candidal and others - are observed with HIV infection.
Candidal lesions of the mucous membranes oropharynx are the most frequent complications antibiotic therapy. They are usually combined with lesions of the entire oral mucosa. On the tonsils, less often on the arches and, as a rule, on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, which takes on a dark red color, whitish dot deposits appear, which, merging, form a whitish-grayish film. IN severe cases when the films are removed, an eroded bleeding surface is exposed. In most cases, there is no pain when swallowing, the temperature does not rise, and regional lymph nodes do not increase. When the larynx is affected, hoarseness, aphonia, and difficulty in breathing appear. Perhaps a combination of lesions of the mucous membrane with skin and visceral forms: bronchopulmonary, intestinal and candidal sepsis.
enanthems on the mucous membrane of the soft palate can be with measles, chicken pox, mosquito fever, typhus (Rosenberg's enanthema).
Changes in oropharynx are also found in some acute intestinal infections. Thus, in typhoid fever, swelling and redness of the tonsils are often observed from the first days of the disease. It can be so pronounced that they even talk about typhoid sore throat (A.F. Bilibin). In the 2nd week of typhoid fever in individual cases Duguet's ulcerative tonsillitis is observed: small ulcerations without raids appear on the tonsils and arches. Changes in the oropharynx are accompanied by coated tongue (the edges and tip of the tongue are free from raids), roseolous rash, enlargement of the liver and spleen, bloating, fever of various types.
In many patients erythema multiforme exudative mucous membranes are also affected, but in combination with damage to the external genital organs. Painful bleeding erosions appear on the mucous membrane of the pharynx, larynx, nose, oral cavity, urethra. The disease can recur and be accompanied by new rashes that are more severe than the previous ones.
Combined lesions mucous membrane of the oropharynx, skin and other organs are observed in a number of chronic infections: syphilis, tuberculosis, leprosy. In some patients with syphilis and tuberculosis, the lesion of the oropharynx may be the only clinical manifestation illness.



