Presentation on solar and lunar eclipses. Solar and lunar eclipses
slide 1
Solar and lunar eclipses.
slide 2

Solar eclipse
A solar eclipse is an astronomical phenomenon in which the Moon completely or partially obscures the Sun from an observer on Earth. A solar eclipse is possible only on a new moon, when the side of the moon facing the Earth is not illuminated, and the moon itself is not visible. Eclipses are possible only if the new moon occurs near one of the two lunar nodes(points of intersection of the apparent orbits of the Moon and the Sun), no more than about 12 degrees from one of them.
slide 3

The shadow of the moon on the earth's surface does not exceed 270 km in diameter, therefore solar eclipse observed only in a narrow band in the path of the shadow. Since the Moon revolves in an elliptical orbit, the distance between the Earth and the Moon at the time of an eclipse can be different, respectively, the diameter of the lunar shadow spot on the Earth's surface can vary widely from maximum to zero (when the top of the cone of the lunar shadow does not reach the Earth's surface). If the observer is in the shadow band, he sees a total solar eclipse in which the Moon completely hides the Sun, the sky darkens, and planets and bright stars can appear on it.
The shadow of the Moon on Earth during an eclipse, photograph from the ISS. The photo shows Cyprus and Turkey.
slide 4

The totality of a solar eclipse is also expressed by the phase Φ. The maximum phase of a partial eclipse is usually expressed in hundredths of a unit, where 1 is the total phase of the eclipse. The total phase can be greater than unity, for example 1.01, if the diameter of the visible lunar disk is greater than the diameter of the visible solar disk. Partial phases have a value less than 1. At the edge of the lunar penumbra, the phase is 0. The moment when the leading / trailing edge of the Moon's disk touches the edge of the Sun is called touchdown. The first contact is the moment when the Moon enters the disk of the Sun (the beginning of the eclipse, its partial phase). The last touch (fourth in case of a total eclipse) is last moment An eclipse is when the moon leaves the disk of the sun. In the case of a total eclipse, the second touch is the moment when the front of the Moon, having passed all over the Sun, begins to exit the disk. A total solar eclipse occurs between the second and third touches. In 600 million years, tidal drag will push the Moon away from Earth enough to make a total solar eclipse impossible.
slide 5

slide 6

Around the solar disk hidden by the Moon, one can observe the solar corona, which is not visible under the usual bright light of the Sun. When the eclipse is observed by a stationary ground observer, the total phase lasts no more than a few minutes. The minimum speed of the lunar shadow on the earth's surface is just over 1 km/s. During a total solar eclipse, astronauts in orbit can observe the moving shadow of the Moon on the Earth's surface. Observers close to the total eclipse may see it as a partial solar eclipse. During a partial eclipse, the Moon passes across the disk of the Sun not exactly in the center, hiding only part of it. In this case, the sky darkens much weaker than during a total eclipse, the stars do not appear. A partial eclipse can be observed at a distance of about two thousand kilometers from the zone of total eclipse.
Slide 7
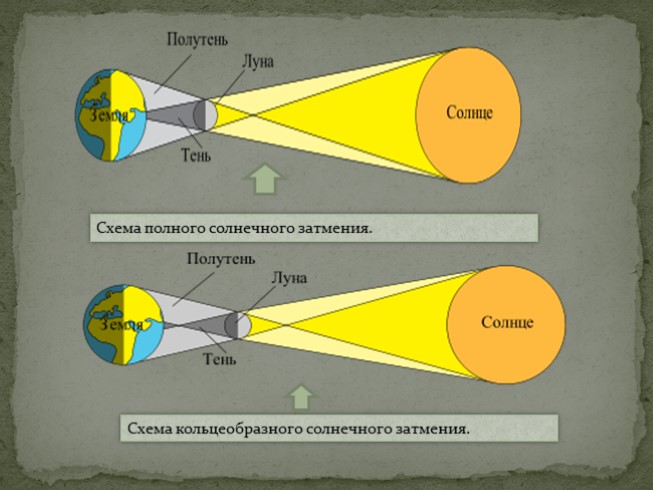
Diagram of a total solar eclipse.
Diagram of an annular solar eclipse.
Slide 8

The frequency of solar eclipses In a year on Earth, from 2 to 5 solar eclipses can occur, of which no more than two are total or annular. On average, 237 solar eclipses occur in a hundred years, of which 160 are partial, 63 are total, and 14 are annular. At a certain point on the earth's surface, eclipses in the major phase occur quite rarely, and total solar eclipses are even more rare. So, on the territory of Moscow from the 11th to the 18th centuries, 159 solar eclipses with a phase greater than 0.5 could be observed, of which only 3 were total (August 11, 1124, March 20, 1140 and June 7, 1415). Another total solar eclipse occurred on August 19, 1887. An annular eclipse could be observed in Moscow on April 26, 1827. A very strong eclipse with a phase of 0.96 occurred on July 9, 1945. The next total solar eclipse is expected in Moscow only on October 16, 2126.
Slide 9

Numerous displays of a solar eclipse on the ground in the shade of tree foliage, due to the camera obscura effect created by light passing through the small gaps between the leaves.
Slide 10

Phenomena during a solar eclipse Shadow waves (running shadows, English shadow bands) Bailey's rosary Diamond ring Crescent shadows (Camera obscura) Decrease in atmospheric temperature Glow ring
slide 11

Moon eclipse
A lunar eclipse is an eclipse that occurs when the Moon enters the cone of shadow cast by the Earth. The diameter of the spot of the Earth's shadow at a distance of 363,000 km (the minimum distance of the Moon from the Earth) is about 2.5 times the diameter of the Moon, so the entire Moon can be obscured. At each moment of the eclipse, the degree of coverage of the Moon's disk by the Earth's shadow is expressed by the phase of the eclipse F. The phase value is determined by the distance 0 from the center of the Moon to the center of the shadow. AT astronomical calendars the values Ф and 0 are given for different moments of the eclipse. When the Moon during an eclipse completely enters the shadow of the Earth, they speak of a total lunar eclipse, when partially - a partial eclipse. The two necessary and sufficient conditions for the onset of a lunar eclipse are the full moon and the proximity of the Earth to the lunar node.
slide 12

slide 13

As seen by an observer on Earth, on the imaginary celestial sphere, the Moon crosses the ecliptic twice a month at positions called nodes. The full moon can fall on such a position, on the node, then you can observe a lunar eclipse
.
Slide 14

Total eclipse A lunar eclipse can be observed on half of the Earth's territory (where the Moon is above the horizon at the time of the eclipse). The view of the darkened Moon from any point of observation is negligibly little different from another point, and is the same. The maximum theoretically possible duration of the total phase of a lunar eclipse is 108 minutes; such were, for example, the lunar eclipses of August 13, 1859, July 16, 2000.
slide 15

During an eclipse (even a total one), the Moon does not disappear completely, but becomes dark red. This fact is explained by the fact that the Moon, even in the phase of a total eclipse, continues to be illuminated. Sun rays, passing tangentially to the earth's surface, are scattered in the earth's atmosphere and, due to this scattering, partially reach the moon. Since the earth's atmosphere is most transparent to the rays of the red-orange part of the spectrum, it is these rays that reach the surface of the moon during an eclipse to a greater extent, which explains the color of the lunar disk. In fact, this is the same effect as the orange-red glow of the sky near the horizon (dawn) before sunrise or just after sunset. The Danjon scale is used to estimate the brightness of an eclipse. View of the Moon during a lunar eclipse An observer located on the Moon at the time of a total (or partial, if he is on the shaded part of the Moon) lunar eclipse sees a total solar eclipse (an eclipse of the Sun by the Earth).
Municipal State Educational Institution Voznesenskaya Secondary School
Solar and lunar eclipses
Natural History Project
Performed:
6th grade student
Chernomorets Julia
Teacher:
Tkachenko Svetlana Viktorovna
Supervising teachers:
Bulova Elena Stepanovna
v. Voznesenka, 2015
Tasks:
- Learn what a solar and lunar eclipse is.
- Learn about solar and lunar eclipses.
- Find out what effect eclipses have on living organisms.
Objective of the project:
investigate the causes of solar and lunar eclipses.
Solar and lunar eclipses
The property of the rectilinear distribution of light is explained by the formation of shadows from opaque objects when they are illuminated. When the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, the moon's shadow falls on the earth's surface. A total solar eclipse can be observed in the region of the Moon's shadow. In those places on the surface of the Earth in which the Moon covers only part of the disk of the Sun, a partial eclipse of the Sun is observed. When the Earth is between the Sun and the Moon, a shadow from the Earth falls on the surface of the Moon and a lunar eclipse is observed.
Solar eclipse
A solar eclipse is an astronomical phenomenon, which consists in the fact that the Moon closes (eclipses) completely or partially the Sun from an observer on Earth. The moon's shadow on the earth's surface does not exceed 270 km in diameter, so a solar eclipse is observed only in a narrow band along the path of the shadow. If the observer is in the shadow band, he sees a total solar eclipse in which the Moon completely hides the Sun, the sky darkens, and planets and bright stars can appear on it.
Diagram of a solar eclipse
From 2 to 5 solar eclipses can occur on Earth per year
Moon eclipse
A lunar eclipse that occurs when the Moon enters the shadow cast by the Earth. The diameter of the spot of the Earth's shadow is about 2.5 diameters of the Moon, so the entire Moon can be obscured. The view of the darkened Moon from any point of observation is negligibly little different from another point, and is the same. The maximum theoretically possible duration of the total phase of a lunar eclipse is 108 minutes
For calendar year 0 to 3 lunar eclipses occur.
Diagram of a lunar eclipse
Types of lunar eclipses
penumbral
Usually, even before the onset of a Lunar and Solar eclipse, a negative cosmic influence is felt not only on the psychological, but also physiological state person. A few days before and after the eclipse, the number of people who begin to seek help from psychotherapists with mental problems and different kind mental disorders.
Besides, in given period there is a deterioration in well-being not only in patients, but even in practically healthy people. Persons who have chronic diseases, note the exacerbation of diseases. There are complaints of unreasonable anxiety, excitement, insomnia, increased blood pressure, heart palpitations, etc.
Elderly, weather-sensitive people are especially susceptible to this.
It was noted that during a solar eclipse, more men turn to doctors, and during a lunar eclipse - women.
Nature also reacts to eclipses - earthquakes and other natural disasters are possible a week before and a week after.
The activity of the World Ocean is increasing - it is during eclipses that a greater number of storms and tsunamis occur.
Not only people feel the adverse effects of eclipses, but also animals. At this time, the animals become restless, you can see that their behavior changes, as if they anticipate trouble.
Why are solar and lunar eclipses dangerous for humans?
Solar and lunar eclipses in literary works.
solar eclipse in Ancient Russia was too significant a phenomenon to be "not noticed" or chronologically rearranged. Therefore, all solar eclipses fell into the annals. Including the solar eclipse on May 1, 1185 during the campaign of Igor Svyatoslavich against the Polovtsians.
A. Volkov "The Wizard of the Emerald City" - during a solar eclipse, a hurricane took away Ellie's house.
"Robinson Crusoe" - the crash of a ship during a storm caused by a solar eclipse.
Observation of the lunar eclipse in the village. Voznesenka December 10, 2011
Conclusions:
Solar and lunar eclipses are proof of the straightness of the propagation of light rays. Solar eclipses occur more often than lunar ones.
Eclipses affect people, especially the elderly and weather-sensitive, and living organisms.
Sources of information:
- A. E. Gurevich, D. A. Isaev, L. S. Pontak, “Natural science grades 5-6”, textbook. Publisher M .: "DROFA", 2013, 191 pages.
- O.F. Kabardin, "Physics Grade 8", textbook. Publishing house M.: "Enlightenment", 2013, 176 pages.
- V. Kasyanov, V. Dmitrieva, "Physics Grade 8", workbook. Publishing house M.: " open world", 1998, 127 pages.
Electronic sources of information:
4. Center esoteric knowledge"Aquilon". [Electronic resource]. Influence of eclipses 2001 - 2015. http://akviloncenter.ru/books/
summary of other presentations"Astronomy News" - Teaching Methods. Methods of teaching astronomy. The science that deals with the study of cosmic bodies. Appearance time. Worldview. Branch of science. Teaching astronomy. The study of astronomy yesterday and today. Teaching astronomy. Astronomy. Suggestions for teaching astronomy in the future.
"Space exploration by man" - Launch vehicles are divided into disposable and reusable. US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) - 1958. Space agencies. The satellite had the shape of a ball with a diameter of 58 cm and a weight of 83.6 kg. A crater named after Gagarin reverse side Moon. Communication of stations with the Earth is carried out spaceships Soyuz type. Milestones: Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) - 2003.
"Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin" - In memory of Yuri Alekseevich Gagarin, patriot and citizen. Everyone was close and dear to me.” (Yuri Gagarin, "The Road to Space"). "Star son of Russia". The presentation was experimentally held in one of primary school. The time spent in space was 108 minutes. Brief annotation. Information about the authors of the project. April 12, 1961 The presentation contains autobiographical data about cosmonaut Yu. A. Gagarin, a patriot of his country.
"Sergey Korolev" - And the Moon really turned out to be solid ... But "much to do" was no longer possible. The space age is our time. Already in 1934, Korolev's book "Rocket flight in the stratosphere" was published. And since 1946, S.P. Korolev began work on the creation of powerful ballistic missiles. The operation turned out to be fatal - Sergei Pavlovich died. Then S.P. Korolev wrote: "The moon is solid, S. Korolev." The doctor said, "Well... twenty years, I think."
"Solar and lunar eclipses" - Solar and lunar eclipses. Close connection eclipse with the zodiac was noticed by the ancients. The phases of the moon repeat with a period of 29.53 days (synodic month). Eclipse types. When photographing the eclipsing Sun, astronomers use thick filters. Photo by Vladimir Shatovsky. Total solar eclipse March 29, 2006. Part 4. Periodicity of eclipses. The apparent path of the Moon intersects the apparent path of the Sun (the ecliptic).
Here you can download finished presentation about solar and lunar eclipses. Presentation subject: Astronomy. Colorful slides and illustrations will help you to interest your classmates or audience. To view the contents of the presentation, use the player, or if you want to download the presentation, click on the appropriate text under the player. The presentation contains 11 slides.
Presentation slides
The Earth-Moon system of the ISS is being modernized, 20.09.2006
planets solar system Earth group not big sizes and mass high average density slow axial rotation few (no) satellites solid surface Giant planets large size and mass low average density (comparable to H 2 O) fast axial rotation big number ring satellites powerful H-He atmosphere Space Age On October 4, 1957, the first satellite (Sputnik-1, USSR) was launched. April 12, 1961 the first manned flight into space (Yu.A.Gagarin, USSR, spacecraft “Vostok”). Observation of the bodies of the Solar System, in addition to optical ones, has been carried out by various spacecraft for the last more than 40 years. At the origins of the beginning of the space age is Russia. The first cosmonaut of the planet Yuri Alekseevich Gagarin (1934 - 1968) The founder of the theory of jet propulsion Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (1857-1935) The founder of Russian cosmonautics Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (1907-1966) The designer of jet engines Valentin Pavlovich Glushko (1908-1990) 12.04.1961. Baikonur. Launch vehicle 8K72 ("Vostok") before launch. First ISS. A ball with a diameter of 58 cm and a weight of 83.6 kg 17.11. 19 70, AMS "Luna-17" delivered to the Moon "Lunokhod-1" 11/15/1988, the Soviet MTKK "Buran" on the ground. Earth Earth - the third planet from the Sun, is quite massive and holds an atmosphere near it. Which consists of: A rare phenomenon - mother-of-pearl clouds. Photo in Antarctica by Rene Baker at Antarctic Mawson Station on the evening of July 25, 2006. Air temperature in the cloud area is -87°С, wind speed is 230 km/h. They consist of ice crystals at an altitude of 20-30 km. Basic movements of the Earth Movement around the Sun in an elliptical (close to circular, e=0.0167) with an average speed of 29.8 km/s. The radius of the Earth's orbit -149.6 million km - is taken as one astronomical unit. The orbital period is 365.256 days or one year. Rotation around the axis Changing the time of day. The axis of rotation all the time // to itself and is inclined to the plane of the orbit at an angle of 66 ° 34 ". As a result, the seasons change. Shape of the Earth By 1684 I. Newton proved that the Earth is compressed along the poles (ellipsoid). Size determination was first carried out in 240 BC in Egypt by Eratosthenes. Grandiose measurements from the Arctic Ocean to the Danube were carried out in Russia in 1816-1855 under the leadership of V.Ya. Struve. Later it was found out that the shape of the Earth has a more complex figure - the geoid (pear-shaped). Equatorial radius 6378 km Polar radius 6356 km. The average radius is 6371 km. Compression is 0.0034 Compression e \u003d (a-b) / a, where a is the major, b is the minor semi-axis of the ellipse Knowing the size of the Earth, you can determine its mass and average density, considering the Earth approximately a ball F = m. g \u003d G (M . m) / R 2 M \u003d (g . R 2) / G ≈ 5.9736. 10 24 kg þ cf \u003d M / V \u003d 5.515 kg / m 3 The moon is a satellite of the Earth The moon is turned to the Earth on one side, shines with reflected light, has an ashy color and the type of phase (illuminated part) depends on the relative position of the Sun, Earth and Moon. Phase - the ratio of the area of the illuminated part of the visible disk of the Moon to its entire area (or the thickness of the illuminated part of the disk to its diameter). If the view of the crescent moon (mentally substitute a wand and get the letter p) - the month is young (the moon is growing). If the crescent of the moon is - the month is old (the moon is waning). The full cycle of phase change (synodic month) is approximately 29.5 days. The Moon makes a full revolution around the Earth (sidereal month) in about 27.3 days. The moon quickly moves across the sky from west to east: 360 o: 27.3≈13 o / day Every day the culmination is delayed by 24 hours: 27.3≈50 min . Because of the large size, the Earth-Moon system is called a double planet and the center of mass is located at a distance of 4671 km from the center of the Earth (it is he who moves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit). a=384400km e=0.0549 R=1738km Eclipses An eclipse is a phenomenon in which light from a celestial body is temporarily obscured by another body. This may be for our solar system: 1) the passage of a planetary satellite (for example, the Moon), in the shadow of the planet so that no light falls on it (for example, the Sun); 2) dimming of the entire luminary (for example, the Sun) or part of it by a satellite passing in front of it (for example, the Moon - a solar eclipse). During the month favorable for eclipses, one solar eclipse or two solar and lunar eclipses can occur. The next location of the lunar orbit necessary for eclipses will occur only after half a year (177-178 days) The maximum number of eclipses per year is seven (for example, 1982 - four partial solar and three total lunar) eclipses of the Moon and four partial eclipses of the Sun, although one of the solar eclipses was very small. It is theoretically possible that there will be solar eclipses on two successive new moons, and a lunar eclipse between them. However, lunar eclipses on two successive full moons are not possible. Eclipses are repeated (Egyptian - saros), which is associated with the rotation of the plane of the lunar orbit. The small saros is 6585.32 days (18 years 10.32 days). During this time, there are 70-71 eclipses (42-43 solar and 28 lunar) and in the next saros eclipses are repeated in the same order. In any saros series, each eclipse occurs approximately 8 hours later and nearly 120° of longitude west of the previous eclipse. The big saros is 19756 days (54g 34 days) - a repetition of almost identical eclipses, which changes over the course of 1000 years in a different series. Scheme of a solar eclipse The orbit of the Moon is inclined to the plane of the Earth's orbit by 5.1 °, so from time to time these three bodies are in conjunction. Then an eclipse occurs. Solar eclipse Types of solar eclipse: 1. private - closes part of the solar disk, 2. annular - completely covers the Sun when the diameter of the Moon is less than the solar one, 3. total (central) - completely covers the Sun when the diameter of the Moon is greater than the solar one. A solar eclipse occurs on a new moon or a close point in the orbit, the maximum duration is 7 minutes 40 seconds. The shadow draws a curved trajectory on the Earth's surface with a maximum width of 264 km (the penumbra is about 6000 km), moving at a speed of 1 km/s. Partial eclipses can also occur when a total eclipse is not observed at any point on the Earth. The sequence of phases of the annular solar eclipse on December 24, 1973 (period 1.5 hours) During the brief moments of a total solar eclipse, darkness sets in and the outer parts of the Sun, the chromosphere and corona, become visible, the light of which is usually drowned in the bright light of the photosphere. Total eclipse March 29, 2006 Photo by cosmonauts Valery Tokarev and William MacArthur from the ISS The condition for the onset of a solar eclipse is that at the time of the new moon, the Moon crosses the ecliptic. Total solar eclipse March 29, 2006 Lunar eclipses Lunar eclipse July 16, 2000 Types of lunar eclipse: 1. partial - the shadow of the Earth covers part of the moon. 2. full - the shadow of the Earth completely covers the moon. A lunar eclipse occurs on or near the full moon with a maximum duration of 1 hour 44 minutes. The reddish color of the Moon's disk is due to the fact that red and orange rays pass through the atmosphere best. Scheme of the onset of a lunar eclipse



